
Understanding and interpreting operating income is essential for making informed financial decisions in today’s complex and dynamic marketplace. Operating profit is a useful and accurate indicator of a business’s health because it removes any irrelevant factor from the calculation. Operating profit only takes into account those expenses that are necessary to keep the business running. This includes asset-related depreciation and amortization, which result from a firm’s operations. Operating profit serves as a highly accurate indicator of a business’s health because it removes all extraneous factors from the calculation.
What are Direct Costs?
Operating income is often used to compare operating margins year-over-year or to competitors. This is a simple way to see how efficiently a company is generating profit from its core operations. The formulas involved in managerial accounting serve the goal of helping the management understand the effect of their decisions and choose courses of action that will benefit the business. Some of the key formulas try to answer questions like how much does a customer need to sell to break even or how much effect will the item have on total profits.
- The average company loses more than 20% of its productive capacity to organizational drag — the structures and processes that consume valuable time and prevent employees from getting things done.
- To calculate income from operations, just take a company’s gross income and subtract the operating expenses.
- Since service companies don’t produce goods, the COGS is replaced by the cost of revenue, which is essentially the COGS for service companies.
- A business’s operating expenses are costs incurred from normal operating activities and include items such as office supplies and utilities.
- As such, operating income is a critical tool in the arsenal of any business manager or owner.
Understanding Operating Profit
In the given case, only $500,000 is operating revenue as it is only related to the core activity of the business, and profit on the sale of equipment is not a part of operating revenue. Net operating income is a profitability metric used to calculate the gains made from an income generating property. It is calculated by deducting operating expenses of the property from the operating revenue. The easiest way to calculate operating income starts with calculating gross income first.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
This is an important concept because it gives investors and creditors an idea of how well the core business activities are doing. It separates the operating and non-operating revenues and expenses to give external users a clear picture of how the company makes money. Operating income includes expenses such as costs of goods sold and operating expenses. However, operating income does not include items such as other income, non-operating income, and non-operating expenses. Importantly, operating income excludes “non-operating” income and expense items that are not technically part of the core business operations, but can be significant.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Return on investment is equal to income made from the investment divided by the amount invested. This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions. There are different ways to calculate using the EBIT formula, although they all come to a common conclusion. Let us understand the steps to calculate the Net Operating Income theory with the help of Colgate Example.
Operating Profit vs. Other Profit Measures
Companies may be more interested in knowing their operating income instead of their net income as operating income only incorporates the costs of directly operating the company. Operating income can be calculated several different ways, but it is always found towards the bottom of a company’s income statement. Operating income is generally defined as the amount of money left over to pay for financial costs such as interest or taxes. Operating income is what is left over after a company subtracts the cost of goods sold (COGS) and other operating expenses from the sales revenues it receives. However, it does not take into consideration taxes, interest or financing charges.
Operating profit is also referred to colloquially as earnings before interest and tax (EBIT). However, EBIT can include non-operating revenue, which is not included in operating profit. If a company doesn’t have non-operating revenue, EBIT and operating profit will be the same figure. Items such as taxes, interest income, non-operating income, and extraordinary gains or losses are not included in the operating income calculation. Operating income is a reflection of a company’s ability to convert its expenses into profits through efficient allocation of its resources. As an illustration, in the earlier example, ABC’s increase in profits came at the expense of losses in its income statement.
Operating income is the profit a company is left with after paying for all expenses related to core business operations. It’s a simple way to measure performance year-over-year or to compare one business to another. Operating income a beginner’s guide to the post-closing trial balance is an earnings “level” on the income statement, sitting below the operational part of the income statement. It’s the next level of revenue refinement after gross profit since it includes the non-direct costs of creating the revenue.
Operating income can also be used to compare the performance of different business units or divisions within a company. By comparing the operating income of different units, managers can identify areas of strength and weakness and make informed decisions about resource allocation and strategic planning. There are a few key ways to improve operating profit, which include reducing the cost of goods, improving inventory management, boosting staff productivity, and increasing the average order value. A company can increase its operating profit by reducing the cost of goods and services it sells.
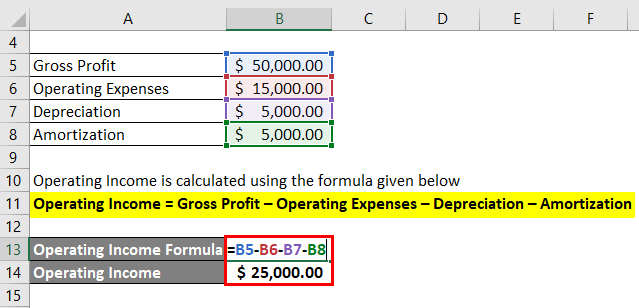
Operating income is gotten from the gross income after deducting operating expenses. Operating profit is calculated by taking revenue and then subtracting the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, depreciation, and amortization. Net income also includes all expenses and revenue that are seen in operating income such as gross income, depreciation, sales expenses and administrative expenses.
